Reading_Notes
OOP:
What is the object?
Because we use programming to make our real world easier.. Every real object can be represented by a programming object that has a state and behavior
>>Through the class we form a primitive structure of the object.
public class Bicycle {
// the Bicycle class has
// three fields
public int cadence;
public int gear;
public int speed;
// the Bicycle class has
// one constructor
public Bicycle(int startCadence, int startSpeed, int startGear) {
gear = startGear;
cadence = startCadence;
speed = startSpeed;
}
If we have a set of objects that are combined with characteristics and behaviors.
—> Its organization can be facilitated by inheritance, building a base object and deriving others from it
>> Class group can be organized using the package
What is the interface?
The interface is a contract between the code and the outside world .. where the results of operations are shown in an understandable way for any user
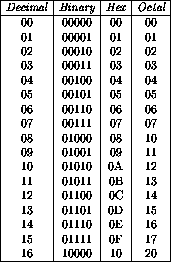
Numbers system:
Decimals:
a decimal number has a “position” ,it also called “Base 10”:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9
Binary Numbers:
“Base 2” numbers instead of “Base 10” , so its has just 0 and1 numbers.
Hexadecimal Numbers:
“Base 16”, they look the same as the decimal numbers up to 9, but then there are the letters ("A',"B","C","D","E","F") in place of the decimal numbers 10 to 15.