Reading_Notes
In memory storage:
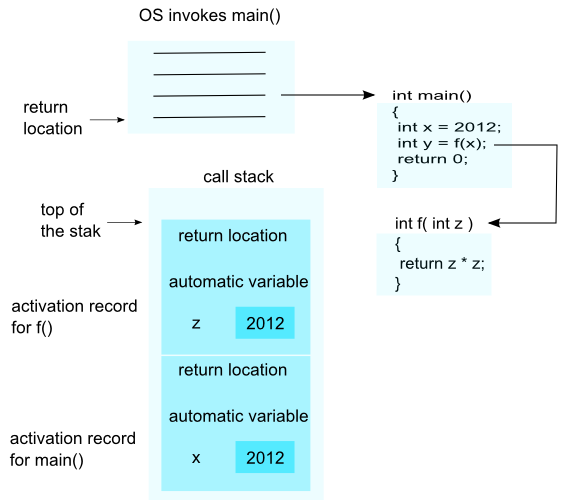
Understanding the JavaScript Call Stack
What is a ‘call’?
A call is a function invocation, and a call stack is a hierarchy and ordering of these calls.
##How many ‘calls’ can happen at once? Calls in a call stack happen one at a time, from top to bottom.
What does LIFO mean?
LIFO is an abbreviation for last in, first out. It is a method for handling data structures where the first element is processed last and the last element is processed first.
Draw an example of a call stack and the functions that would need to be invoked to generate that call stack.
What causes a Stack Overflow?
The most-common cause of stack overflow is excessively deep or infinite recursion, in which a function calls itself so many times that the space needed to store the variables and information associated with each call is more than can fit on the stack
JavaScript error messages
What is a ‘refrence error’?
In JavaScript, a reference error is thrown when a code attempts to reference a non-existing variable.
What is a ‘syntax error’?
An exception caused by the incorrect use of a pre-defined syntax. For example, if you leave off a closing brace ( } ) when defining a JavaScript function, you trigger a syntax error.
What is a ‘range error’?
A RangeError is thrown when trying to pass a value as an argument to a function that does not allow a range that includes the value. This can be encountered when: passing a value that is not one of the allowed string values to String.
What is a ‘tyep error’?
The TypeError object represents an error when an operation could not be performed, typically (but not exclusively) when a value is not of the expected type. A TypeError may be thrown when: an operand or argument passed to a function is incompatible with the type expected by that operator or function; or.
What is a breakpoint?
At each breakpoint, JavaScript will stop executing, and let you examine JavaScript values. After examining values, you can resume the execution of code (typically with a play button).
What does the word ‘debugger’ do in your code?
The debugger keyword stops the execution of JavaScript, and calls (if available) the debugging function. This has the same function as setting a breakpoint in the debugger. If no debugging is available, the debugger statement has no effect. With the debugger turned on, this code will stop executing before it executes the third line.